Type II diabetes model
Diabetes (DM) is a kind of metabolic disease that seriously threatens human health. Due to insulin secretion defects or dysfunction, the body's chronic blood sugar levels increase, leading to metabolic disorders of sugars, proteins, fats, etc., which in turn cause chronic damage to tissues and organs such as the kidneys and heart
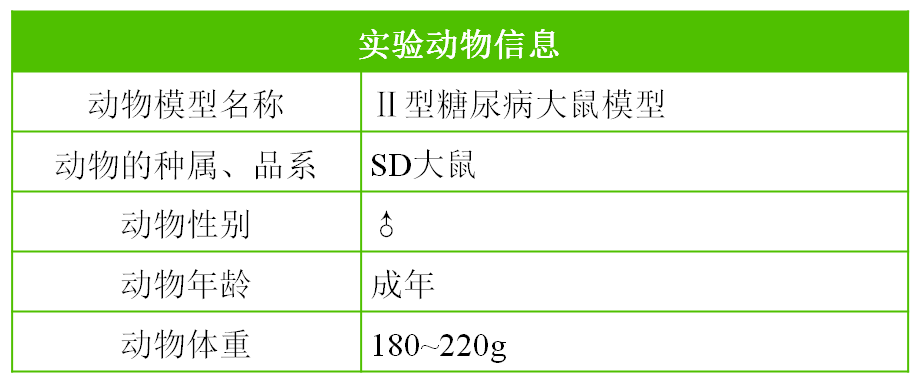
Type II diabetes rat model
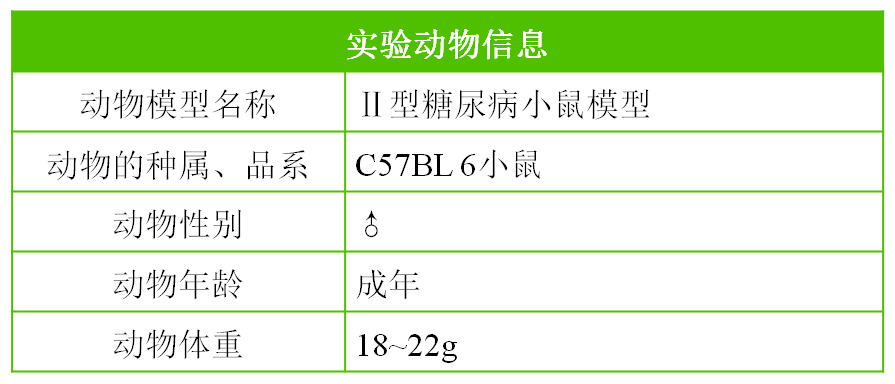
Type II diabetes mouse model
Observation indicators
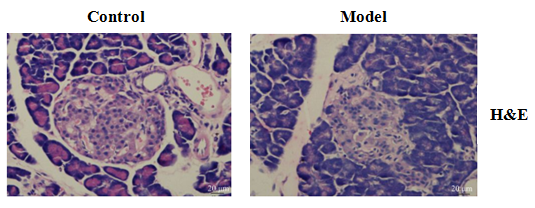
Compared with the control group, blood sugar increased, serum triglycerides (TG), cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein (HDL-C), free fatty acids (FFA), glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) increased, and insulin significantly decreased; Pancreatic and renal tissues show varying degrees of pathological changes.
Partial Results Display